
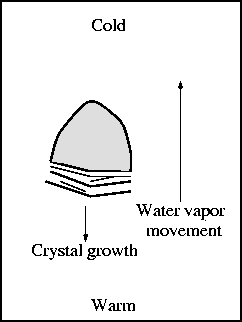
Crystals growth
- Sublimation process: vapor <-> crystal
- Grow into regions with high water vapor content
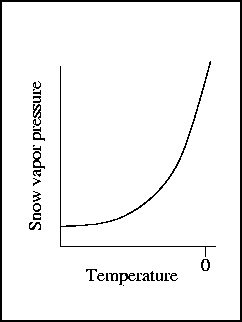
- Snow vapor pressure grows with temperature
- functional relationship on the right
- large gradient near zero
- At warmer temps, larger supply of vapor for growth
- Crystals favor sharp corners to dissipate latent heat
- Surface tension forces sharp corners to round off
Temperature dependence
- Temperature gradients differentiate preferred growth
- Gradients in temperature imply vapor pressure gradients.
p = f(T) or dp = f'(T) dT
- At low temps, small pressure gradient since f'(T) is small
- Ground temperature is freezing, surface temperature lower
- Mean temperature gradient, (surface temp)/(snow depth)
- Much larger near surface
Constructive metamorphism vs. Destructive metamorphism
- Interplay between crystal growth and destruction
- Constructive metamorphism (surface and depth hoar)
- If dp is large enough, crystals grow
- Crystals in the pack grow down
- Crystals remain in this state for long times
- Destructive metamorphism
- If dp is small, surface tension smooths grains